Bibliometric measures are data about publications, or citation frequency.
Scientometrics is the branch of information science concerned with the application of bibliometrics to the study of the spread of scientific ideas; the bibliometric analysis of science.
Definitions adapted from Oxford English Dictionary Online
Image: By en:user:Ael 2, vectorized by pl:user:Vulpecula (vectorized version of File:H-index_plot.PNG) [Public domain], via Wikimedia Commons
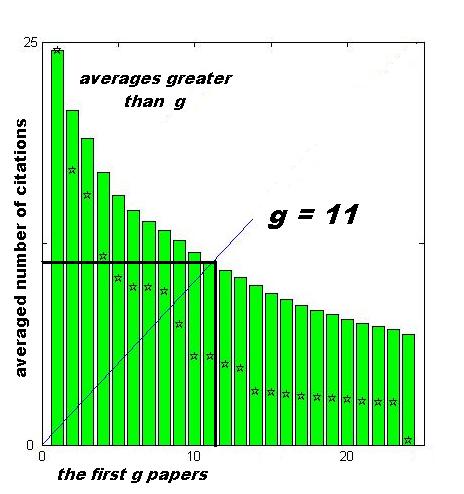 g-index: The average of citations matched by the number of articles rather than the number of citations matched by the number of articles
g-index: The average of citations matched by the number of articles rather than the number of citations matched by the number of articlesImage: By Ael 2 (Own work) CC BY-SA 3.0, via Wikimedia Commons
Citation counts: The number of citations to an article, using citation data indexed in that database -- i.e., Scopus or Web of Science -- or, in the case of Google Scholar, collected by its algorithm
Field-Weighted Citation Impact (Scopus): The number of citations received by a document divided by the expected number of citations for a similar document
Altmetrics: Online usage and discussion of a scholarly article
Article Influence (uses Web of Science citation data; in Journal Citation Reports or at http://www.eigenfactor.org)
Eigenfactor (uses Web of Science citation data; in Journal Citation Reports or at http://www.eigenfactor.org)
CiteScore: Eight indicators to analyze the publication influence of serial titles
Source-Normalized Impact per Paper (SNIP): Measures contextual citation impact by taking differences in disciplinary characteristics into account; can be used to compare journals in different fields.
Scientific Journal Rankings (SJR): Weights the value of a citation based on the subject field, quality and reputation of the source
The Journal Citation Reports database maintains the original "journal impact factor" calculations for journals in their index, which finds the ratio of published documents to citations in a given JIF year.
The image here is a screenshot of a journal's impact favor calculated for the JCR year and how it compares to other journals in the same field.

